Of the water resources on Earth, about 97 percent is salt water while only about 3 percent is freshwater. These resources are found in groundwater and in different bodies of water and provide the water that animals, plants, and people need. People harness these resources in various ways for use in their households and for agriculture, industries, and recreation.
Groundwater
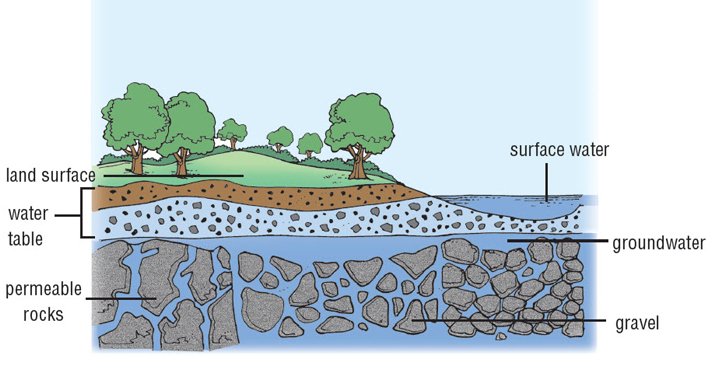
Groundwater is water that is found beneath the surface of Earth, between the layers of soil and rocks. It is stored in areas under the ground called aquifers. An aquifer contains mostly gravel and permeable rocks, or rocks through which liquids and gases seep and therefore can hold water for sometime. Its topmost part is known as the water table.
Part of the water that falls on the ground through rain and snow is absorbed by the permeable rocks and is added to the water in the aquifer. The water table rises during heavy rains or snow and subsides during drier periods. From the aquifer, the water finds its way to the ground’s surface either naturally through springs or by being extracted through human-made artesian wells. The water in the springs then flows out to bigger bodies of water such as streams, rivers, and lakes while the water that is pumped out through wells is used primarily for irrigation, for domestic uses, and in industries.