Changes in the Different States of Matter
Matter can change or transform from one state to another. A change in the state of matter is an example of physical change. The water cycle is the perfect example of matter changing states.
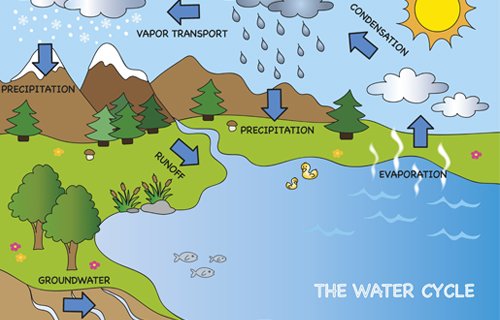
First, water in liquid form is found in bodies of water. Then, the heat of the sun allows it to evaporate, turning it into water vapor, which is gas. When precipitation happens, water falls back to the earth, either as liquid (rain) or solid (hail, snow, or sleet).
Matter can change or transform from one state to another through melting, evaporation, condensation, solidification, and sublimation.
Melting
When solids are heated, their particles vibrate and gain more energy. This vibration causes them to expand and break away from their positions. This is the condition when melting point is reached. Melting point is the temperature at which solids turn into liquids.
Different solids have different melting points. When ice is placed under the sun, it will absorb radiant energy and start to become liquid. The process by which solids change to liquids due to the addition or absorption of heat is called melting.
