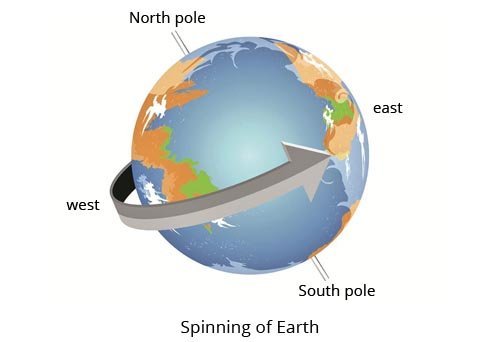
Rotation
Earth spins on a counterclockwise direction or from west to east. This explains why you can observe the sun rising in the east and setting in the west. The rotation or spinning of the Earth occurs on its axis, or the imaginary line that passes through the poles at which Earth rotates. Earth's axis is not straight up or down. it is tilted or slanted by 23.5° relative to vertical.
Earth rotates at a speed of 1674.4 kmh. At this rate, Earth makes a complete rotation on its axis in approximately 24 hours or one day, based on the time it takes for the sun to appear on the same spot in the sky. This rotation period is called a solar day, or the time between noon of one day and noon of the next, that is, between two successive appearances of the sun directly overhead.
During the interval, Earth moves along its orbit, or path around the sun, so the sun appears to move eastward in the sky. As a result, Earth finishes almost one complete rotation before the sun crosses the same meridian, or line running from pole to pole, again.
Earth actually takes 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4.09 seconds to turn once on its axis with respect to the background stars. This is called a sidereal day, based on the time between the passage of a given star across a particular meridian and the next passage of that star across the same meridian. A solar day, therefore, is approximately 4 minutes longer than a sidereal day.